Purpose of constructor is to assign values to instance variables at the time of object creation.
Constructor gets invoked(to call) at the time of object creation.
Constructor looks like a method without return.
Constructor name should be class name.
TYPES OF CONSTRUCTOR:
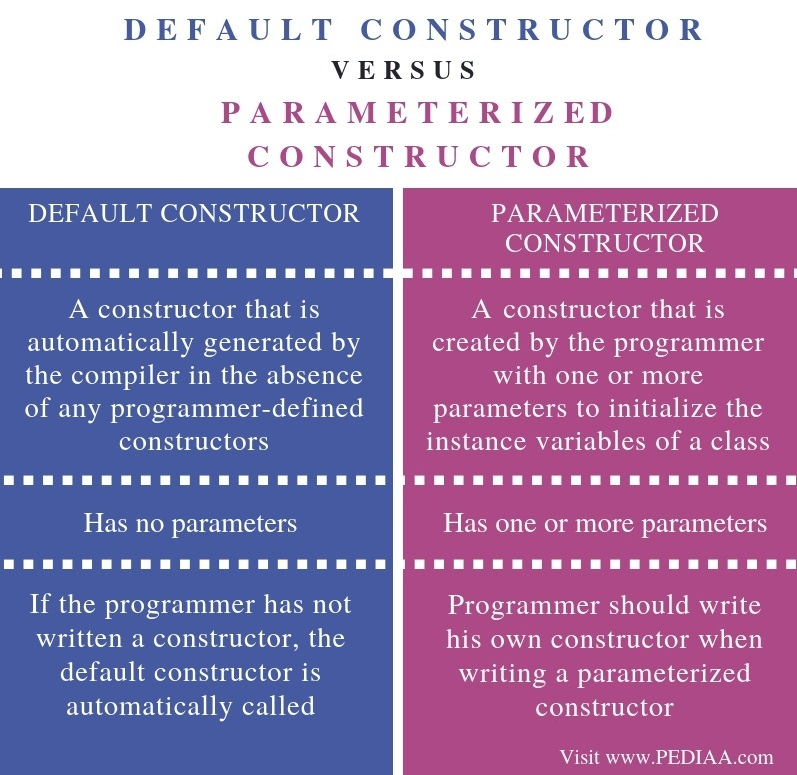
Default constructor:
Default constructor is to assign default values to instance data variables when there is no parameterized constructor as well as values not assigned to instance varibles.
Default constructor works automatically if it couldn’t find a parametrized constructor in a program and there is no values assigned for instance variables.
We no need to write constructor.
eg: new primeNumber();
Parametrized constructor:
Parameterized constructor is to assign values to instance data variables passed during object creation.
We need to build a constructor.
eg: new Students(1, “Ram”, 74.0);

EXAMPLE FOR CONSTRUCTOR:
public class Students
{
int rollno;
String name;
double percentage;
void printGrade()
{
//insert code here
}
//CONSTRUCTOR
Students(int a, String b, double percentage)
{
rollno=a;
name=b;
percentage=c;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
Students S1= new Students(1,”sam”,78.0);
Students S2= new Students(2″ram”,75.0);
Students S3= new Students(3″zara”,98.0);
S1=printGrade();
S2=printGrade();
S3=printGrade();
}
}
SOME BASIC QUESTIONS ON CONSTRUCTOR TO BE LEARNED:
- Why we need constructor in java?
We do not require to call the constructor manually. It automatically invokes implicitly during the instantiation.
In other words, a constructor is a method that is called at runtime during the object creation by using the new operator. The JVM calls it automatically when we create an object. When we do not define a constructor in the class, the default constructor is always invisibly present in the class.
In short, we use the constructor to initialize the instance variable of the class.
2. Why there is no return type for constructor?
return- to store value in the compiler’s memory.
Constructor is just an intermediate between values and instance variable, it makes use of local variables to assign/pass on the variables. So, there is no need of returning anything as output.
3. Why constructor should have same name as class name?
Constructor call has to identify the instance variables present inside the class with the help of class name. So, the constructor name should be same as the class name for easy identification.
4. Purpose of constructor:
The one and only purpose is to assign values to instance variable.
5. Can constructor be overloaded?
YES, constructor can be overloaded because we won’t have the same number of parameters.
6. How many constructor can be placed inside a class?
A class can have any number of parameters.
7. Can overriding happens in constructor?
No, it ends in compiler error because two class cannot have same name.
Leave a comment